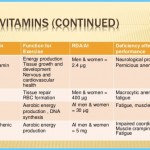
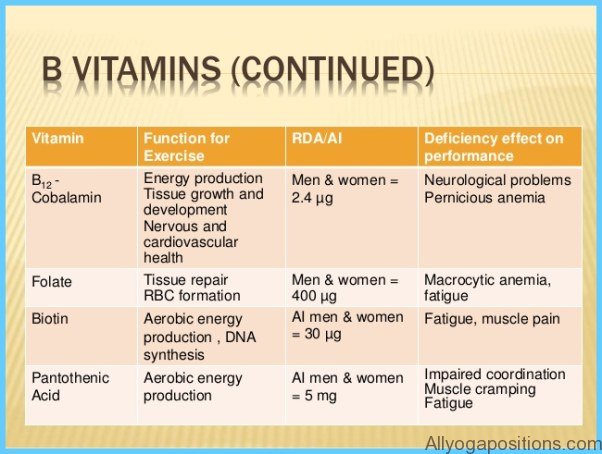
Without B vitamins our bodies would lack energy. These eight nutrients are indispensable for yielding energy compounds from the foods we eat. Many B vitamins serve as helpers to enzymes that release energy from fat, protein and carbohydrate. As
you’ll read later, an optimal intake of certain B vitamins may help to reduce the risk of heart disease and cancer.
The following lists the B vitamin family, how much you need and where to look for it.
B VITAMINS for Women Photo Gallery
B VITAMIN RDA FOR WOMEN AGED 19+ BEST FOOD SOURCES
Thiamin (B1) 1.1 milligrams pork, ham, bacon, liver, whole-grain or enriched breads and cereals, dried peas, beans and lentils, nuts
Riboflavin (B2) 1.1 milligrams milk, yogurt, cottage cheese, meat, leafy green vegetables, whole-grain or enriched breads and cereals
Niacin (B3) 14 milligrams milk, eggs, poultry, fish, whole-grain or enriched breads and cereals, nuts, all protein-containing foods
B6 1.3 to 1.5 milligrams whole grains, bananas, potatoes, legumes, fish, meat, poultry
Folate 400 micrograms spinach, orange juice, lentils, asparagus, artichokes, avocado, leafy greens, wheat germ, whole grains
B12 2.4 micrograms meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, eggs, fortified soy and rice milk
Biotin 30 micrograms widespread in foods
Pantothenic acid 5 milligrams widespread in foods
Reprinted with permission from Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folate, Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, Biotin and Choline,
Copyright © 1998 by the National Academy of Sciences. Courtesy of the National Academy Press, Washington, D.C.
To ensure you are getting your fair share of B vitamins, take a good quality multivitamin and mineral supplement each day.
If you’re looking for more B vitamins than a regular multi gives you, choose a “high potency” or “super” formula that contains 30 to 75 milligrams of B vitamins (or micrograms in the case of folic acid). You can also take a B complex formula that gives you all eight B vitamins, often combined with vitamin C. One word of caution: the B vitamin niacin could cause flushing of the face and chest when taken in doses greater than 35 milligrams (this can be avoided by taking your supplement just after eating a meal). This symptom is harmless and goes away within 20 minutes, but some people find it uncomfortable. To avoid flushing, look for a formula that contains niacinamide—a non-flushing form of niacin.
Vitamin B6
The body uses B6 to form an important enzyme that’s needed to create serotonin, a chemical in the brain that has a calming and relaxing effect. Healthy women need 1.3 to
1.5 milligrams of the vitamin each day. The best sources of B6 are high-protein foods like meat, fish and poultry. Other good sources include whole grains, bananas and potatoes.
B6 in Foods
FOOD VITAMIN B6 (MILLIGRAMS)
Beef, flank, cooked, 3 oz (90 g) 0.3 mg
Pork center loin, cooked, 3 oz (90 g) 0.3 mg
Chicken breast, cooked, half (140 g) 0.3 mg
Chicken leg, cooked (187 g) 0.2 mg
Salmon, sockeye, cooked, 3 oz (90 g) 0.2 mg
Tuna, canned and drained, 3 oz (90 g) 0.4 mg
100% bran cereal, 1/2 cup (125 ml) 0.5 mg
Cereal, whole-grain flakes, 2/3 cup (160 ml) 0.5 mg
Avocado, Florida, half medium 0.4 mg
Avocado, California, half medium 0.2 mg
Banana, medium 0.7 mg
Potato, baked, medium with skin 0.7 mg
Nutrient Values of Some Common Foods, Health Canada, Ottawa, 1999.
B6 Supplements
If you’d like to try a daily supplement, reach for a 50- to 100-milligram pill once a day. Because the eight B vitamins work together, I recommend a B complex supplement. Taking only one B vitamin in high doses could upset the body’s balance. Don’t take more than 100 milligrams each day, since too much vitamin B6 can cause irreversible nerve damage.