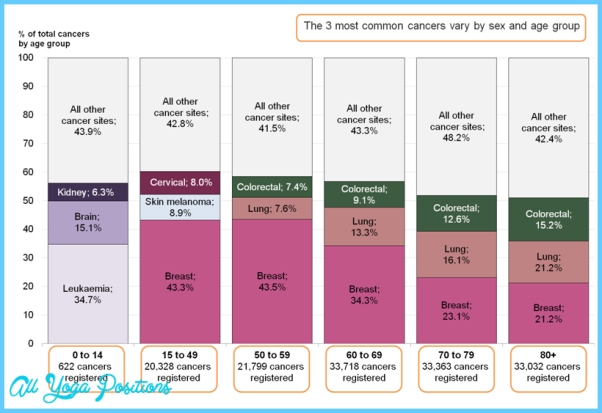
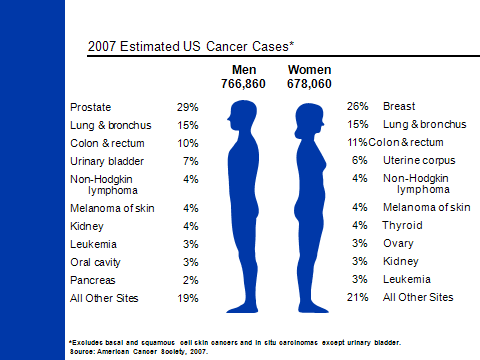
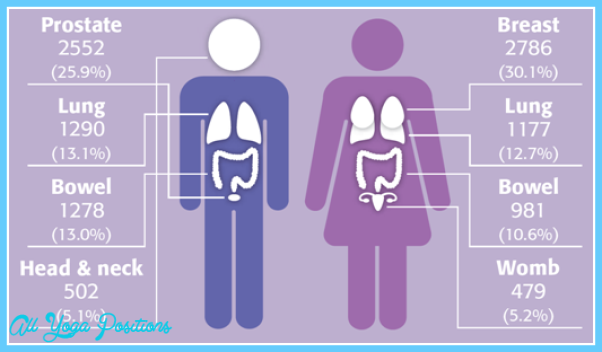
COMMON CANCERS
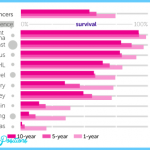
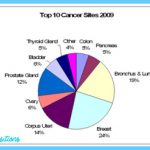
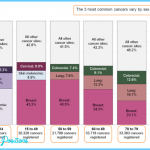
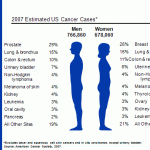
Each year, more than 1.5 million Americans are diagnosed with cancer, and more than 580,000 die (Figure 12.2). These statistics exclude the more than 1 million cases of the curable types of skin cancer. At current U.S. rates, nearly one in two men and more than one in three women will develop cancer at some point in their lives. Nearly 14 million living Americans have a history of cancer.
Until 1991, the number of cancer deaths increased fairly steadily in the United States, largely due to a wave of smoking-related lung cancers in men. In 1991, the death rate began to fall slowly; since then it has dropped more than 19% in men and 11% in women. Still, many more people could be saved from cancer. The American Cancer Society (ACS) estimates that 90% of skin cancer could be prevented by protecting the skin from the rays of the sun, and 87% of lung cancer could be prevented by avoiding exposure to tobacco smoke.
A discussion of all types of cancer is beyond the scope of this book. This section looks at the most common cancers and their causes, prevention, and treatment.
Lung Cancer
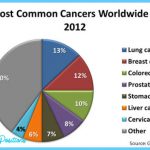
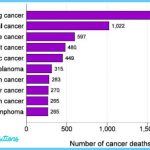
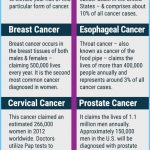
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer death in the United States; it is responsible for about 159,000 deaths each year. Since 1987, lung cancer has surpassed breast cancer as the leading cause of cancer death in women.
The chief risk factor for lung cancer is tobacco smoke, which currently accounts for 30% of all cancer deaths and 87% of lung cancer deaths. When smoking is combined with exposure to other carcinogens, such as asbestos particles, the risk of cancer can be multiplied by a factor of 10 or more. Quitting substantially reduces risk, but ex-smokers remain at higher risk than those who never smoked. And the smoker is not the only one at risk. Long-term exposure to
Tumor A mass of tissue that serves no physiological purpose; also called a neoplasm.
COMMON CANCERS Photo Gallery
Benign tumor A tumor that is not cancerous.
Malignant tumor A tumor that is cancerous and capable of spreading.
Lymphatic system A system of vessels that returns proteins, lipids, and other substances from fluid in the tissues to the circulatory system.
Metastasis The spread of cancer cells from one part of the body to another.
Carcinogen Any substance that causes cancer.
Wellness Tip
If you smoke, find a way to stop. There are many options for quitting smoking. See Chapter 13 for advice on giving up tobacco. environmental tobacco smoke (ETS), or secondhand smoke, also increases risk for lung cancer. ETS causes about 3400 lung cancer deaths in nonsmoking adults each year.
Symptoms of lung cancer usually do not appear until the disease has advanced to the invasive stage. Signals such as a persistent cough, chest pain, or recurring bronchitis may be the first indication of a tumor’s presence. Lung cancer is most often treated by some combination of surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy; if all the tumor cells can be removed or killed, a cure is possible. Lung cancer is usually detected only after it has begun to spread, however, and only about 15% of lung cancer patients are alive five years after diagnosis.