GELATIN
Gelatin can be your best assistant to create just the right amount of delicious whipped fillings with perfect texture and firmness in cakes and pastries, powder, leaves and instant gelatins. It would not be an exaggeration to say that the secret of the ready-made, creamy, soft sliceable cakes or pastries that you love that taste is in a tablespoon of gelatin. Well, where else do we come across gelatin, whose name we are starting to hear more and more? Gelatin also creates a wonderful creamy mouthfeel, even with reduced-fat fillings, and technically, gelatin can both increase product shelf life and improve freeze-thaw stability. And that’s not all, it can help you increase the crispness of waffles and biscuits with gelatin.
Dairy products and desserts
In yogurts, gelatin prevents syneresis and whether you want a creamy or firm consistency, anything is possible with gelatin. Gelatin also helps creams and sauces retain their appeal, provides easy gliding and superior melting properties of sour cream and cheese, and gives semi-skimmed butter its fat-like texture.
How does gelatin do all this? Gelatin can bind water and is a versatile emulsifier and stabilizer.
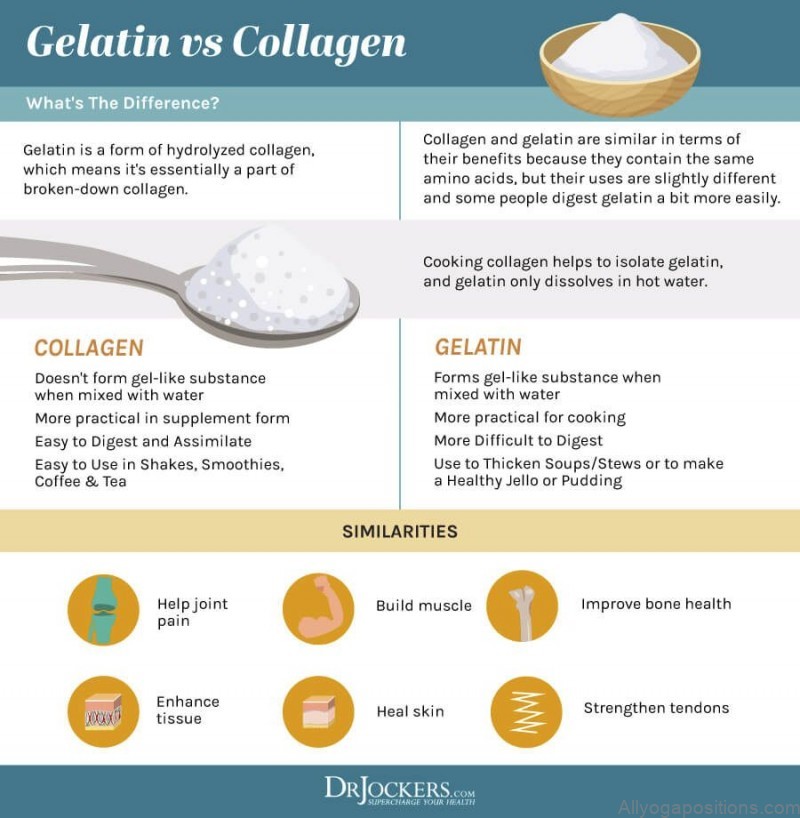
What is gelatin? Everything You Need to Know Photo Gallery
What is gelatin?
Gelatin is a protein substance. Gelatin is derived from collagen found in mammalian tissue, the attachment points of muscles and bones and other organs, and the skin. It produces from skin, bone and connective tissue of animals with long production processes. There are 2 different production processes to obtain gelatin; acid and alkali method. To obtain gelatin, collagen undergoes alkaline hydrolysis (type B gelatin) or acid hydrolysis (type A gelatin).
Gelatin is a very powerful food in terms of amino acids. Since its structure constitutes 84-86% of the protein, it is a protein-rich food.
It can mimic the “oily” mouthfeel and is perfect for low-fat, semi-oily or even non-oily products. It can even make creamy skim ice cream a reality without other additives.
Collagen proteins in meat products Slicable meat products and sausages can be produced with the help of gelatin. For edible skins, suitable special gelatins with the necessary adhesive properties are available. High-quality collagen proteins to optimize technological and sensory quality parameters – for example to reduce the amount of preserved sausage jam and fat, to improve the spread properties of the sausage, to enrich the protein content to optimize the texture of boiled sausage or to accelerate ripening in the production of raw sausage meat available.
Gelatin is a protein whose structure consists of collagen. It has many health benefits due to its unique amino acid content.
Studies have shown that “gelatin” has many beneficial effects, especially on joint health, brain functions, skin and hair appearance.
Gelatin for Everyone What is gelatin?
Gelatin is obtained by cooking tissues rich in collagen obtained from animals. Most of it is protein and it has many health benefits thanks to its rich amino acid structure. Collagen is a type of protein commonly found in humans and animals. It is found almost everywhere in the body, especially in the skin, bone, tendons and connective tissues.
The elasticity and strength in the structure of the tissue come from collagen. When consumed regularly, it strengthens the structure of tissues with its increase in the body. But it is also difficult to consume. Because there is not much in the edible meat parts of the animal, it is not easy to consume with meals. Of course, by boiling certain parts of the animal in water, different meat dishes and soups can be made with this collagen water. However, it is unclear how much quality and absorbable collagen is consumed, even if it is consumed in the form of trotter soup.
Fortunately, we can obtain collagen from animals by certain technical methods. In this way, we can easily use it in powder or liquid form. Although this type of collagen is available in the markets, mostly large food companies and companies that make collagen supplements show demand for this pure gelatin. This industrial type is usually gelatin colorless and odorless. It turns into a gel-like consistency when dissolved in water and begins to cool slightly.
When gelatin is processed, a substance called collagen hydrolyzate is produced. As this gelatin is used as a supplement, it has the same health benefits as gelatin. When you mix this substance with water, this time it does not get a gel-like consistency, so it is more suitable to be used as a supplement. Both gelatin and collagen hydrolyzate are available as supplements in powder or granule form.
Protein
The majority of gelatin, 84-86%, is protein. Gelatin, which contains many essential amino acids, can also contribute to the daily protein need in a quality way. Although there is no rule for daily gelatin intake in our daily diet, we know that we need daily protein and indirectly amino acids. While completing this, gelatin, that is, collagen, can also be a healthy protein source alternative.
The richest amino acids found in gelatin:
Glycine: 27%
Proline: 16%
Valine: 14%
Hydroxyproline: 14% Glutamic acid: 11%
These values may vary slightly depending on the animal tissue used or the way of preparation. Yes, it is not a very rich source of vitamins and minerals, but the uniquely rich amino acids in its content make gelatin a valuable food.
Gelatin is the richest source of the amino acid “glycine”. Studies show that although our bodies can produce glycine, it can be supplemented when it’s not enough. It supports the production of creatine, which is necessary for the muscles to obtain energy more easily, especially in sports. In addition, since it is a very powerful antioxidant, it also helps to protect the body against aging and disease.
Importance of gelatin for joint and bone health
The positive effects of the use of gelatin and collagen in its structure have been observed in studies conducted especially on those with joint and bone disorders (for example, osteoarthritis). Osteoarthritis is one of the most common osteoarthritis conditions and its treatment is long and difficult. In such cases, in addition to physical therapy or doctor interventions, nutrition has a special importance in treatment.
In a study of 80 people with osteoarthritis that lasted for 70 days, they were given either gelatin supplements or a placebo. As a result, it was determined that joint stiffness and pain decreased clearly in the gelatin group. Similar positive studies have also been conducted on athletes. Repeated studies show that gelatin is also effective in pain relief.
However, I would like to remind you that although it supports the treatment of osteoarthritis, it is not a solution on its own. The only complaint in collagen consumption was that it was unpleasant and the feeling of swelling in the stomach.
However, it is scientifically clear that it is a food worth using for joint and bone health.
Effect of gelatin on the appearance of hair and skin shown that people who take gelatin supplements have positive effects on hair and skin. In one study, a female subject group was asked to consume approximately 10 grams/day of collagen. At the end of 8 weeks, there was a 28% increase in skin moisture of women consuming bovine collagen, while a 12% increase was observed in those consuming fish collagen. According to the results of many studies, it has been found that the consumption of gelatin accelerates hair growth and thickens the hair.
The effect of gelatin on weight loss Although the production method of gelatin differs, it generally does not contain fat and carbohydrates, therefore, its calories are very low. Scientific studies show that gelatin has positive effects on weight loss. In one study, 20 grams of gelatin was given to 22 people and as a result, it was reported that there was an increase in hormones known to reduce appetite and it created a feeling of satiety in the stomach.
Effects on Type-2 Diabetes Along with the effect of aiding weight loss, gelatin also has positive effects on Type 2 diabetes, which is one of the main risk factors of obesity. Studies have shown that people with Type 2 diabetes can better control their blood sugar with the consumption of gelatin. For example, in one study, 74 people with Type 2 diabetes were given 5 grams of glycine and a placebo daily for 3 months. As a result of the study, the improvement in HbA1C levels in the group given glycine shows that gelatin may actually be effective in many different disease groups (HbA1C indicates 3-month blood sugar).
To sum up,
Gelatin is rich in protein and has numerous health benefits with its unique amino acid profile. There is ample evidence that gelatin reduces joint and bone pain, improves brain function, and reduces signs of skin aging. Since gelatin is colorless and tasteless, it can be easily consumed in the diet. You can make your own gelatin at home or buy it ready-made to add to your daily food and drinks.
Table of Contents